Investigate the causes of the xenophobia in South Africa, violent attacks on immigrants, and methods to promote harmony and social peace. Includes genuine data, graphs, and solutions.
Recently, xenophobia in South Africa has become more severe as a result of an isolated mindset into a frequent national problem. Despite being the country with the most industrialized infrastructure, South Africa has repeatedly witnessed violence directed at foreign nationals, particularly at immigrants from other African countries.
Among the economic instability, high unemployment, and social division, xenophobic sentiment has increased in prominence- this has led to deadly violence, destruction, and forced travel. While the government acknowledges the violence, there are still significant problems within the system that lead to distrust and hostility towards immigrants.
This article discusses the causes of xenophobia in South Africa, it describes the violent behavior associated with it, and it suggests practical steps towards lasting peace.
What is xenophobia? Xenophobia is the irrational or intense disdain or fear of individuals from other nations. In South Africa, it is expressed through hostility that is often violent, this is directed at African immigrants, specifically those from Zimbabwe, Mozambique, Nigeria, Malawi, and the Democratic Republic of the Congo.
This fear is often attributed to the belief that foreigners take jobs, utilize public services, and commit crime—claims that are not always backed by the facts.
Historical background
The history of South Africa has had a significant impact on the development of xenophobia.
During the apartheid era, isolation led to many South Africans not knowing about African diversity.
Post-1994 democracy facilitated border openings, but it also revealed discrepancies and unsustainable economic expectations.
Immigration policies that are limited cause many people to come into the country illegally.
Cause of Xenophobia in Africa’s southern region
1. Economic Inertia
With the country’s unemployment rate at over 32 percent (2024), many citizens of South Africa consider immigrants to be the cause of the lack of jobs, particularly in informal fields like construction, street trading and domestic work.
” They’re taking our jobs and decreasing the wages we receive” is a popular belief, despite the data that shows that the majority of immigrants have jobs that locals don’t.
2. Overburdened Public Services
Immigrants that are legal or illegal have access to services like healthcare, education and housing, these services add to the already weak systems. This often inspires contempt.3. Political Accuse
Leaders and important figures will sometimes criticize foreigners for criminal behavior, trafficking of drugs, or financial issues. This speech promotes violence and ignores the government’s failures.
4. Social Isolation
Many immigrants choose to live in marginalized areas, such as housing estates or informal settlements, these areas have few opportunities for cultural interaction. This isolation instills suspicion.5. Crippled Law enforcement
The lack of accountability for attacks against immigrants is general. Few of the perpetrators are caught and fewer still are convicted–this encourages retribution.
Timeline of the Major Outbreaks of Xenophobia.
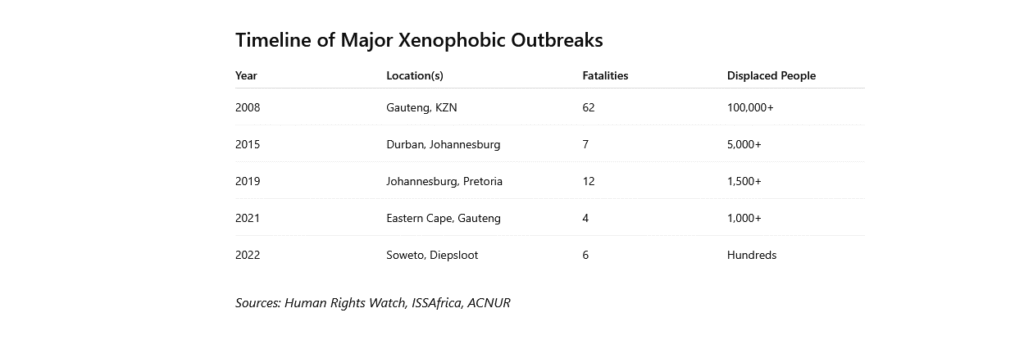
Chart: Violent attacks on ethnic minorities in South Africa (2008-2013)
Who are the victims: the elderly, the children, and the adults? Informal traders from Africa’s three major nations: Zimbabwe, Somalia and Nigeria.
• Spaza shop owners often took or murdered.
•Refugees and seekers for asylum were accommodated in camps or shelters as a result of attacks.
Employees who are illegal in the country are accused of a crime or are said to have stolen jobs.
Social impact
Economic harm
Companies that are destroying
• Expropriated shops were looted or destroyed.
• Tourists are less likely to visit during severe epidemics.
International fame
Condemnation from the AU, the United Nations and other countries surrounding the region.
Diplomatic conflicts with Nigeria, Zambia and Malawi
Humanitarian consequences
Families that are displaced
Overcrowded accommodations for refugees.
Victims who have experienced trauma, especially children, are vulnerable and need special safeguarding.
Government response: insufficient or lacking
Operation Dudula: controversial military-led campaign to deport illegal immigrants, criticized for violence.
• The actions of repatriation following large outbreaks, which are often considered to be accidental.
• Incitement of the majority of perpetrators or leaders who are not punished.
Realistic solutions: routes to harmony
1. Community integration initiatives
promoting cultural interaction, sports, and educational programs in schools that focus on the African ethnic group can reduce fear and increase tolerance.
2. Political responsibility
The necessity of punitively addressing hate speech and discriminatory rhetoric between politics is crucial.
3. More effective law enforcement
Create dedicated units that will prevent and investigate xenophobic violence, this will have a significant impact on the perpetrators.
4. Economic participation for all
Help small businesses, both local and foreign, by offering microcredits and instruction. Deny the common belief that opportunity is a total zero.
5. Change the way regional migration is managed
Create strategies for SADC-wide migration that promote legal, formal migration and reduce irregularity.
Xenophobia in Africa’s southern region is not simply an expression of poverty or staff shortages, it reflects larger issues of inegalitarian, failed assimilation, and political disdain. Violent outbursts are just the apparent expression of a system of tension that must be addressed in a compassionate and structural way.
The route to peace is characterized by inclusion, justice, education, and powerful institutions. South Africa must recognize that African solidarity is not a danger, but rather a catalyst for growth and togetherness.

FAQs
1. What is xenophobia?
Xenophobia is a fear of foreigners that is unfounded and leads to discrimination or violence.
2. What is the reason for the existence of xenophobia in South Africa?
It derives from the economic disappointment, political culpability, and the social alienation of immigrants.
3 who are primarily affected by xenophobia? primarily immigrants from other African countries, including Zimbabwe, Nigeria, Somalia, Malawi, and Mozambique.
4. Is it illegal for immigrants to be undocumented?
No. Many people are considered legal residents, asylees or refugees, but all of them can be targeted.
5. Has the government failed to stop anti-Semitic violence?
Attempts have been unsuccessful and largely ineffective in preventing or punishing attacks.
6. How does the fear of immigrants affect the country’s reputation?
Negatively. It undermines the diplomatic relationship and discourages tourism and investment.
7. How can things be done to prevent future epidemics?
Educate, integrate, justice and cooperation with the community.
